Article
Arthritis Drug Effective Against Untreatable Eczema
Author(s):
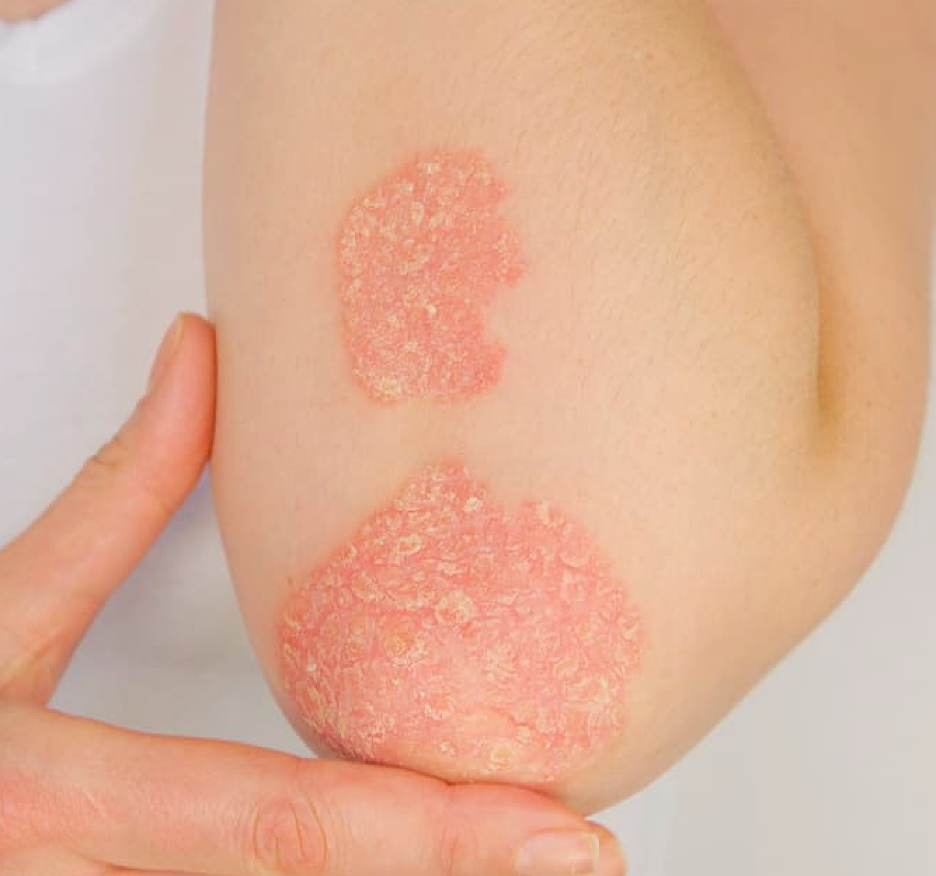
Patients afflicted with moderate-to- severe eczema have been successfully treated with rheumatoid arthritis drug, tofacitinib citrate.
Patients afflicted with moderate-to- severe eczema have been successfully treated with rheumatoid arthritis drug, tofacitinib citrate.
Recently shown to reverse two disfiguring skin conditions, vitiligo and alopecia areata, tofacitinib was also found to interrupt the immune response that causes eczema.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Brett King, MD, from Yale University, and his team demonstrated that compared to traditional therapies, tofacitinib treatment aided in improving symptoms in six patients who were suffering from moderate-to-severe eczema.
All six patients noted significant improvements in sleep, itchiness, and the redness and thickening of skin.
These study results could mean that a change in standard eczema care is on the horizon with targeted therapy. “These individuals were not only very happy with the results, they also expressed a tremendous sense of relief at being comfortable in their skin for the first time in many years,” said King.
Since their current study involved such a small cohort, King and colleagues recommended further research to better understand tofacitinib’s efficacy in long-term care.