Article
Image IQ: Cold Fingers
A 19-year-old woman asked her primary care doctor about something strange that began to occur with her hands: Her fingers were cold and numb during the summer months. What's your diagnosis?
Photo courtesy of VisualDx.
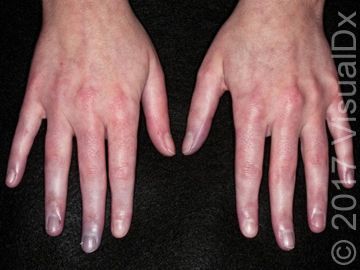
A 19-year-old woman asked her primary care doctor about something strange that began to occur with her hands. It was summer and at her workplace, the air conditioning was kept at frigid temperatures. Her fingers on both hands began to turn white, then blue. They felt cold and kind of numb, but not really painful. These symptoms began weeks ago over the course of a stressful summer.
The patient is showing symptoms of:
A. Raynaud's phenomenon
B. Cryoglobulinemia
C. Cold urticaria
D. Chilblains
Use the VisualDx differential builder to select a diagnosis.
See the next page for the answer.
ANSWER: A) Raynaud's phenomenon
Synopsis
Raynaud phenomenon is a vascular disorder characterized by intermittent arteriolar vasospasm of the digits, most often due to cold temperature or stress. Symptoms present with characteristic changing of hands from white (pallor) to blue (cyanosis) to red (hyperemia), although all 3 phases may not be present in each individual. Raynaud phenomenon may be primary or secondary.
Primary Raynaud phenomenon typically follows a less severe course than secondary Raynaud phenomenon. In primary Raynaud phenomenon, also termed Raynaud disease, vasospasm is not associated with ischemic injury or an underlying associated disease. Primary Raynaud phenomenon typically presents at a younger age (<30 years), involves all fingers symmetrically excluding the thumbs, and is not painful. Patients do not have a history of peripheral vascular disease or ischemic injury. Antinuclear antibody titers are normal or low (<1:40 on indirect immunofluorescence) and nail fold capillaries are normal.
Secondary Raynaud phenomenon is associated with an underlying disease, usually a connective tissue disease of which systemic sclerosis is the most common. Because vasospasm is associated with concurrent ischemia, attacks are typically painful and asymmetric involvement of digits or hands is common. Digital ulcerations or necrosis, digital tuft pits, pterygium inversum, and torturous nail fold capillaries with capillary dropout may be seen.
Additional associations include systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, pulmonary hypertension, frostbite, hematologic malignancies, polyvinyl chloride exposure, cryoglobulinemia, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, repeated trauma / vibration, arteriovenous fistula, intra-arterial drug administration, thoracic outlet syndrome, thromboangiitis obliterans, and Takayasu arteritis.
For more information about this diagnosis, including ICD 10 codes, visit VisualDx.
REFERENCE: This quiz was provided courtesy of VisualDx.