Article
Obesity, Not Diet, Linked to Colonic Diverticula
Author(s):
Obesity, not a low-fiber diet, is more strongly associated with colonic diverticula.
Obesity, not a low-fiber diet, is more strongly associated with colonic diverticula.
Reporting at Digestive Disease Week 2016, researchers said they had looked at patients undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy at the University of North Carolina Hospital in Chapel Hill, NC.
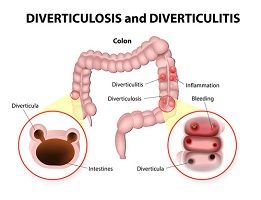
Patients were examined for colonic diverticula.
Of the 451 study participants, 193 (43%) had one or more deverticula (the mean number was 14 and the high number was 158).
Those who did were older, more likely to be male and to have a higher body mass indix and wast to hip ration as well as waist circumference.
The team found no relationship between eating a high fiber diet and the presence or absence of diverticula.
Patients who were obese had a 3.1 times higher risk of diverticula compared to those of a normal weight.
Having a big waist measurement confered a 1.9 times greater risk.
"Dietary fiber intake ws not associated with colonic diverticulosis; obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, significantly increased the risk of diverticulosis," the researchers said.




