Article
Promising Therapy for Vitiligo Treatment
Author(s):
Reports suggest that combination therapy with the drug afamelanotide and narrowband ultraviolet-B ray (NB UVB) phototherapy is safe and effective for restoring skin pigmentation in patients with vitiligo, a skin disease resulting from dead melanin-producing cells with no current cure.
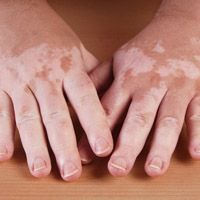
Reports suggest that combination therapy with the drug afamelanotide and narrowband ultraviolet-B ray (NB UVB) phototherapy is safe and effective for restoring skin pigmentation in patients with vitiligo, a skin disease resulting from dead melanin-producing cells with no current cure.
An article published in the Journal of the American Medical Association — Dermatology presented results from a multi-center study involving 55 participants conducted by dermatologists at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, MI, to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the combination of drug and phototherapy treatments for patients afflicted with vitiligo.
Patients were randomized to two groups, with 28 participants receiving combination therapy and 27 individuals receiving only NB UVB phototherapy.
The researchers found that repigmentation occurred after approximately 40 days in the group of participants that received the combination treatment, compared to nearly 60 days for patients who received only phototherapy.
According to the researchers, the combo therapy “should be considered as an option that could significantly enhance the rate and the total surface area of repigmentation.”
The researchers said patients who received combination therapy showed consistent improvement, demonstrating that this treatment has the potential to provide therapeutic benefits for the more than 50 million patients with vitiligo worldwide.
“Our findings offer patients with vitiligo worldwide a renewed hope for a bright future in the treatment of this disfiguring disease,” said Henry Lim, MD, Chair of Dermatology at the Henry Ford Hospital, lead author of the study, and international vitiligo expert. He continued, “Patients with lesions on their face and arms could have a more rapid response to the combination treatment.”
Lim said that afamelanotide “enhances the ability of the UVB to induce repigmentation of the skin.”





