Publication
Article
Family Practice Recertification
Intrauterine System Matches Efficacy of Hysterectomy in Menorrhagia
Author(s):
While a variety of surgical procedures can treat menorrhagia in premenopausal women, a recent study added a non-surgical alternative to the mix.
Review
Heliövaara-Peippo S, et al. Quality of life and costs of levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system or hysterectomy in the treatment of menorrhagia: a 10-year randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Dec;209(6):535.e1-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23999423.
Study Methods
For this 10-year trial, 236 premenopausal women referred to 5 hospitals in Finland for menorrhagia were randomly assigned to either Mirena [levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS)] or hysterectomy as treatment. All of the participants were assessed for health-related quality of life (HRQOL) measures at the time of randomization, as well as at 6 months, 12 months, 5 years, and 10 years.
On average, women in the LNG-IUS group were aged 43.1 years and had 2.1 children, a body mass index (BMI) of 26.6, and menstrual blood loss of 130 ml. Comparatively, those in the hysterectomy group had an average age of 43.1, 2 children, a BMI of 25.1, and menstrual blood loss of 128 ml.
Results and Outcomes
The LNG-IUS and hysterectomy participants experienced similar increases in HRQOL between years 1 and 5. However, those improved HRQOL measures reverted back to baseline levels in both treatment arms between years 5 and 10.
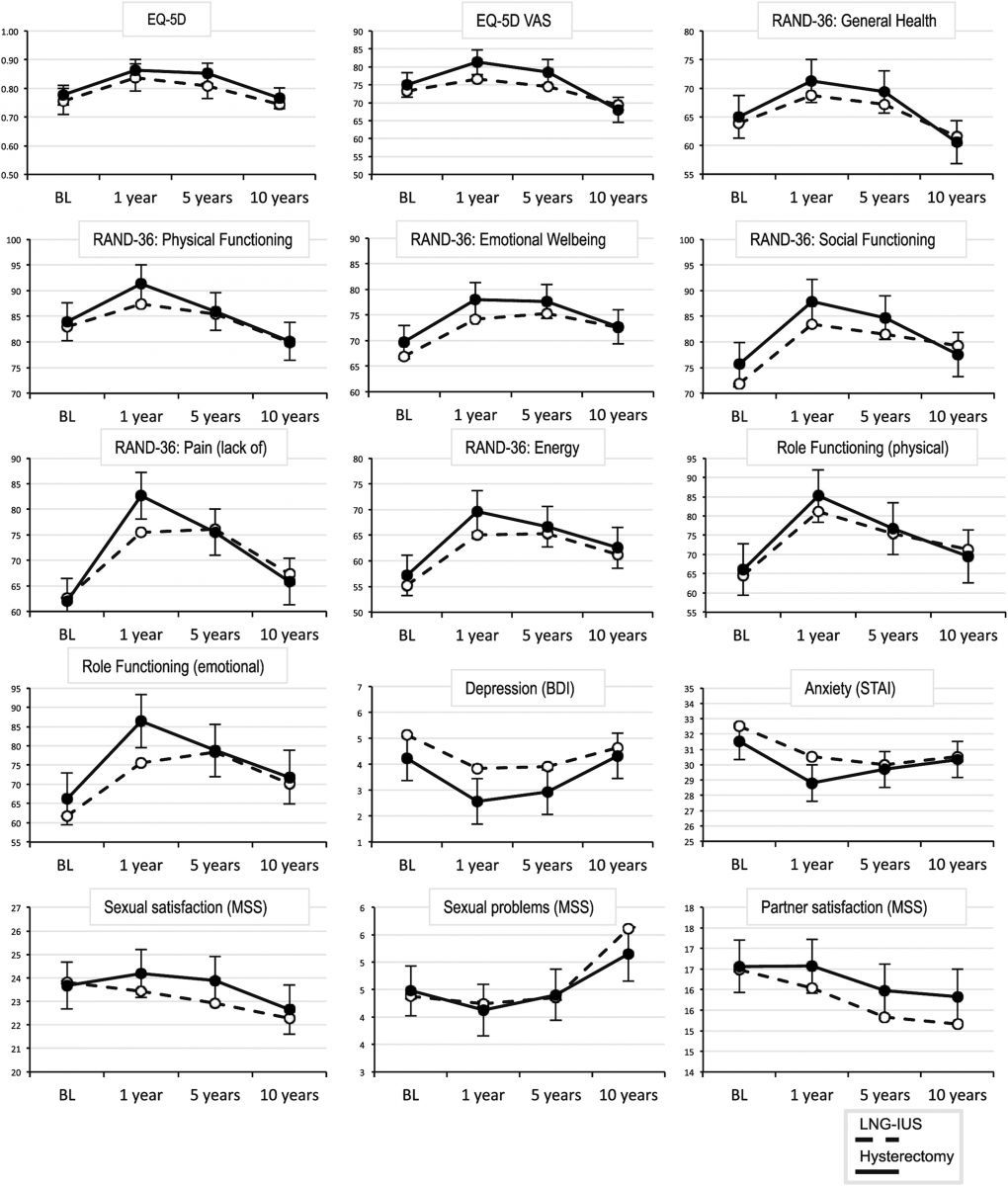
By year 10, nearly half of the LNG-IUS group ultimately underwent hysterectomies, 91% of which were performed within the first 5 years following IUS placement. Nevertheless, the overall costs in the LNG-IUS group were considerably lower compared to the hysterectomy group.
Conclusion
Both LNG-IUS and hysterectomy improved HRQOL measures in premenopausal women with menorrhagia. Although 46% of those randomized to the LNG-IUS arm eventually underwent subsequent hysterectomy, LNG-IUS remained the most cost-effective approach.
Commentary
While a variety of surgical procedures can treat menorrhagia in premenopausal women, this study added a non-surgical alternative to the mix. In addition to substantiating findings from previous studies, it demonstrated a number of new perspectives collected over a lengthy 10-year follow-up period.
In both treatment arms, HRQOL improved in the first 5 years following the LNG-IUS or hysterectomy intervention. However, it is important to note many participants may have reached menopause over the course of the study, so it remains unknown whether their symptoms improved due to the intervention or menopause itself.
Although the participants’ improved HRQOL measures reverted back to baseline levels between years 5 and 10, the authors speculated this decrease paralleled the decline seen in all women as they enter menopause, so it was not related to their method of treatment.
Since a variety of factors can impact a particular patient’s treatment options — including desire for future fertility, risk of carcinoma, tolerance to pain, and level of expectation for symptom relief — family physicians can rest assured that both LNG-IUS and hysterectomy will produce similar outcomes related to HRQOL and feel encouraged to try the LNG-IUS approach, which effectively prevented surgery in more than half of those who received it in this study.
About the Authors
Parisa Samimi, MD, is a recent graduate of the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS) in Worcester, MA.
She was assisted in writing this article by Frank J. Domino, MD, Professor and Pre-Doctoral Education Director for the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at UMMS and Editor-in-Chief of the 5-Minute Clinical Consult series (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins).






